Introduction to the current situation of the enterprise
This paper takes ZH Group as the research object. ZH Group is a large-scale construction engineering group, and its financial information management level has been improved year by year. ZH Group has 21 secondary management organizations and more than 600 management organizations at all levels, with different business models and products, different management models, management styles, organizational structures, and different management priorities and management methods17,18. This paper makes a detailed description of the enterprise’s internal control from the perspectives of the current situation of informatization and the current situation of financial control, and based on this, it describes the informatization financial control system. The specific content is shown in Fig. 1.
Status quo of enterprise informatization and financial control integration.
As can be seen from Fig. 1, ZH’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is now fully established. The enterprise resource planning system is mainly divided into four parts. Firstly, it is an enterprise intelligent operation platform, followed by an organizational supervision platform, which mainly includes a financial sharing platform; Next is the ERP management system, which includes 6 modules, and finally the master data management system. Because the business scope of the group’s internal enterprises is extensive and complicated, the design and implementation of ERP are based on the actual operation and management of each unit. A standard construction guide and specification has been formulated, led by each second-level unit, and centralized deployment in the second-level unit. Combined with the business needs of each legal entity, module selection and implementation are carried out on the standard framework. The ERP system aims to improve the integration of business and finance of individual companies, and according to different operating conditions, improve the integration of business and finance of enterprises, and reduce the amount of manual financial accounting19,20. The group has integrated the accounting system to ensure that the accounting statements of each department are consistent. According to the business management process of the enterprise, it has formulated a standardized process from procurement to payment, sales to collection, production to cost. It also sets up the project promotion team of the ERP Group to support the project construction of various secondary enterprises and ensure the implementation of the standards. In the process of promotion and optimization of ERP projects, there are still unsynchronized launch, different solutions, different products, difficulty in post-optimization, and integration with external systems, as well as many difficulties caused by non-standardization, which affect the overall informatization efficiency of the enterprise.
Overall strategy design of group financial management and control
This chapter takes the group financial control as the core, the information system architecture as the foundation, and the information technology as the foundation. Through the integration of technology and management, breakthroughs have been made in theory and practice. From the perspective of financial management and information system implementation, the overall idea and implementation route are designed, and the overall structure of the entire design is illustrated in the form of graphics, as shown in Fig. 2.
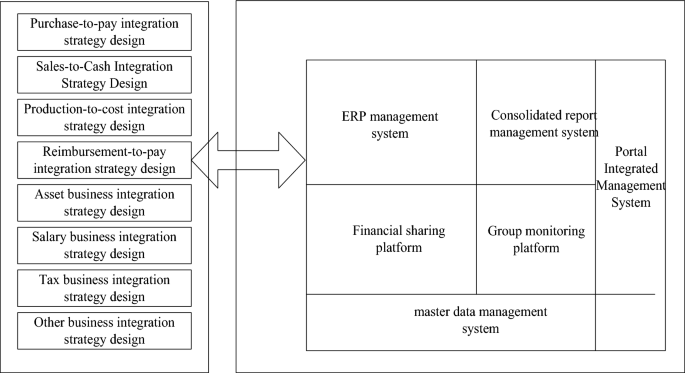
Design diagram of the overall strategy of the group’s financial management and control.
As can be seen from Fig. 2, ZH Group is a large-scale and diversified group. It is difficult for its headquarters to have enough resources to control its subsidiary companies. The financial strategy design of the group is mainly divided into 8 parts, namely procurement and payment integration strategy design, sales and cash integration strategy design, production cost integration strategy design, repayment and payment integration strategy design, asset business integration strategy design, salary business integration strategy design, tax business integration strategy design, and other business integration strategy design. These strategic designs are ultimately integrated into the enterprise resource planning system.It maintains the value of assets through investment, finance and other means. Therefore, financial control is the first choice for enterprise management, and in such a large-scale enterprise, without the support of information technology, it is impossible to realize the financial control of the enterprise21. When considering the design of the group’s overall financial control strategy, people must never leave the perspective of financial management, let alone the information system to design financial control, and the financial control of the group is to meet the business needs of the enterprise by means of information technology.
-
(1)
Strategy design of sales-to-collection integration
Sales is an important business activity, which includes sales plans, sales areas, sales customers, etc., and conducts comprehensive management and statistics on sales volume, sales amount, profit, performance, customer service, etc.22. According to customer data classification, effective management of customer data enables customers to better provide customers with personalized services and improve customer satisfaction. In the sales confirmation stage, including the signing of the sales contract, according to the terms of the contract, it can include prepayment for sales, confirmation of receipt, issuance of sales invoices, and billing and collection. Even if there is no invoice or funding problem, once the ownership of the goods has been transferred, the clearance must be carried out to ensure the accuracy of the clearance. From sales to receipt, the relationship between enterprises and finance can be seen. By reducing, reorganizing, refining, and standardizing the commonality of the entire business process, the overall operational efficiency of the enterprise can be improved.
-
(2)
Strategy design of production-to-cost integration
Production management is the central link of enterprise resource management, which organically combines all the production processes of the enterprise, and combines the procurement management in the material management with the back-end sales management, so that the inventory management of the enterprise is more efficient. At the same time, the original scattered production processes are connected in series, so that the production process of products can flow automatically, so as to achieve continuous production and early warning of product and delivery requirements. Production management is guided by the production plan. According to the pre-established production plan, it is decomposed into executable and standardized work tasks and completed by each production department. During the entire production process, when the entire production process is completed, an enterprise’s inventory can be formed. From the whole process of production and operation to financial expenses, the connection between enterprises and finance can be seen. According to the commonality of the overall business process of the enterprise, the process is tailored, and the process is reorganized. The process tasks are also refined and standardized, so as to improve the overall operation and management efficiency of the enterprise.
-
(3)
Strategy design of other business integration
In addition to some of the more concentrated businesses mentioned, there are many other businesses, which are generally classified as the general ledger of the company23,24. For ZH Group, other businesses based on financial management include fund management, financial investment, special general ledger, financial adjustment, statement management, standard attachment management, etc. In the fund management business, fund settlement runs through all links such as procurement, sales, reimbursement, etc. There is no separate design, and the centralized management of funds included is also carried out within the enterprise.
Realization of group financial control strategy
In the design of the corporate financial control strategy, the design idea of the corporate financial control strategy is expounded in detail, and the corporate design concept is transformed into a concrete implementation, which is linked with the actual management problems of the enterprise. Through the analysis of ZH Group’s strategic design, this paper examines its strategic implementation from the perspective of business logic and system logic, and gives some specific application examples. The implementation of the overall strategy mainly starts from the perspective of financial management and the implementation of the information system, and is classified according to the overall strategy implementation.
-
(1)
Realization of integrated sales-to-collection strategy
In terms of the integration of sales and collection, it is necessary to clearly divide the ERP system, the financial sharing platform, the invoice pool management system, the contract management system and the master data management system, thereby realizing an integrated application from sales to collection. In the comprehensive application, it is necessary to give full play to the functional advantages of each system, and do a good job in the integration management between each system, so as to achieve a better display effect after implementation, as shown in Fig. 3.
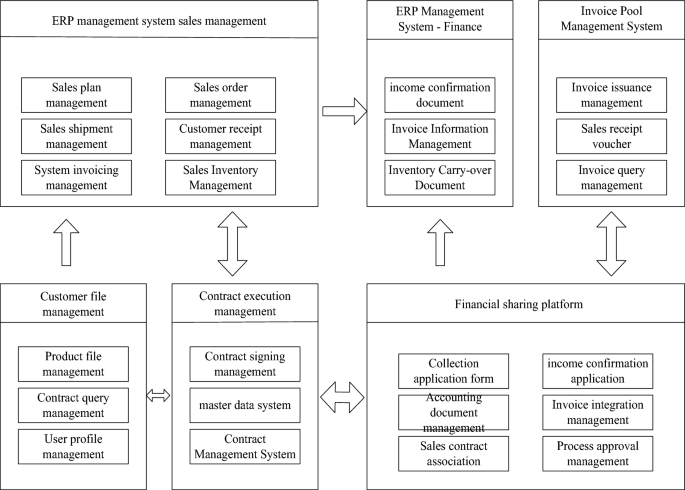
Integration diagram for the implementation of the sales-to-cash integration strategy.
The sales to cash integration strategy in Fig. 3 is divided into 6 modules. The first module is sales management in the ERP management system, the second module is finance in the ERP management system, and the third module is the invoice pool management system; The fourth module is customer file management; The fifth module is contract execution management; The sixth module is the financial sharing platform. The six modules interact with each other, work together, and achieve integration.It can be seen from the integration relationship shown in Fig. 3 that the final result is the management of enterprise customer files, product files, other customer files, etc., as well as the standardization of basic data and user data of each department. At the same time, the main data specifications of the system also lay the foundation for the establishment of contract management and financial sharing platforms. In the contract management system, as the enterprise’s ERP and financial sharing platform, the sales management with ERP is based on the order-based interaction of orders and contracts, while the financial sharing platform is the execution process of the contract, which analyzes the confirmation and execution of the contract’s income, collection, and realizes two-way interaction.
-
(2)
Realization of production-to-cost integration strategy
Combined with the “manufacturing-cost integration” strategic design, in terms of implementation, each functional module of ERP must be combined with the main data management system to form an integrated application from manufacturing to cost25. In the comprehensive application, it is necessary to give full play to the functional advantages of each system, and do a good job in the integration management between the various systems to achieve a better display of the effect after implementation, as shown in Fig. 4:
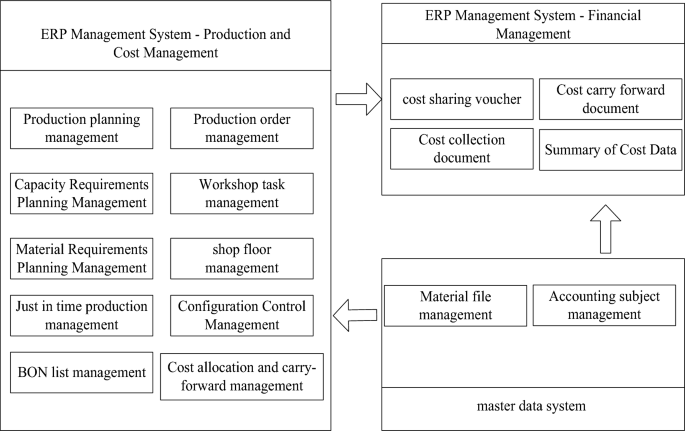
Production-to-cost integration strategy implementation integration diagram.
The production and cost management in the ERP management system in Fig. 4 consists of 10 modules. The production and cost management results obtained from the system are transmitted to the financial management module of the ERP management system. At the same time, the data in the main data system is transmitted to the production and cost management module and the financial management module. The financial management module is responsible for the final financial analysis. It can be seen from the integration relationship shown in Fig. 4 that the final result is that the master data system provides a standardized data basis for the production management module in the ERP system, and standardizes the basic data of each unit. ERP system refers to the front-end management of an enterprise. It integrates its own production and operation functions and financial management functions to form cost allocation vouchers, cost carry-over vouchers, cost collection vouchers, and a summary of cost information.
-
(3)
Realization of other business integration strategies
In terms of other business integration, the group must unify the functions of the financial sharing platform and ERP system and integrate it with other businesses. In the comprehensive application, it is necessary to give full play to the functional advantages of each system, and do a good job in the integration management of each system, so as to achieve a better display effect after implementation, as shown in Fig. 5.
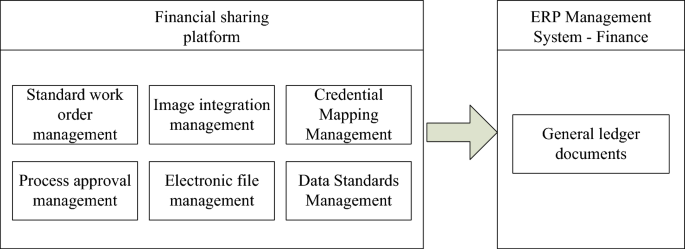
Other business integration strategy implementation integration diagram.
The financial sharing platform in Fig. 5 includes six modules: standard work order management, image integration management, credential mapping management, process approval management, electronic file management, and data standard management. The finance module of the ERP management system is responsible for transmitting the data from these six modules to the finance module and generating the general ledger file. From the integration relationship shown in Fig. 5, it can be seen that the final implementation effect of the system is to use the financial sharing platform to design other types of business, and to use its process approval management, document mapping management and other functions so as to manage other businesses. Through the interface and the financial module of the ERP system, the system is integrated, so that the voucher data is automatically transmitted, and the financial data of the ERP system is more complete26. In financial management, image integration and electronic file management system are used to make file management electronic and visual, establish accounting electronic files, and lay the foundation for remote management of enterprises.
Financial management and risk warning based on intelligent algorithms
In the past few years, overseas scholars have established many prediction models and methods. In recent years, many scholars have introduced artificial intelligence technology in financial risk prediction and improved it. Back propagation neural network is a dynamic model produced by imitating the nervous system of the brain27.
-
(1)
Back propagation (BP) neural network analysis
The famous “error backpropagation” neural network was proposed in 1985, which is a forward-forward neural network with one or more layers28. It not only has the characteristics of parallel processing, distributed storage, fault tolerance, etc., but also has the characteristics of self-learning, self-organization, and adaptability29,30. The BP algorithm does not need to make strict assumptions about the input variables, but just introduces noise into the input variables, with no need to know the relationship between variables and factors, as shown in Fig. 6.
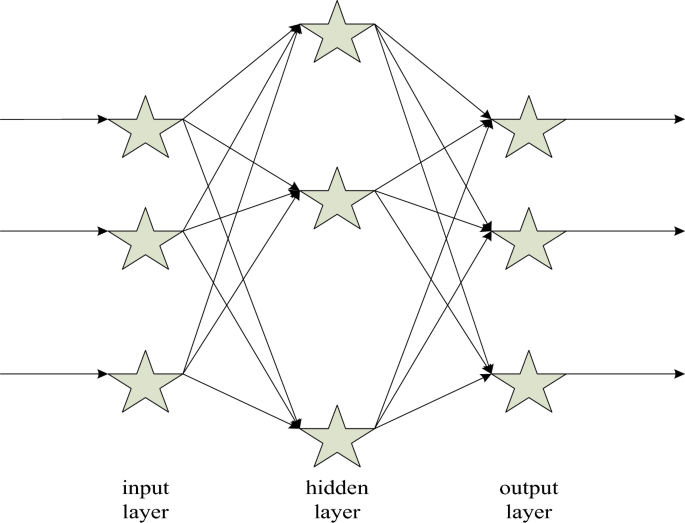
Schematic diagram of BP neural network structure.
From Fig. 6, it can be inferred that the algorithm is as follows. The input variables of the BP neural network are set as Formula 1:
$$X = (x_1 ,x_2 ,K,x_n )^T$$
(1)
Then the corresponding output variable is as Formula 2:
$$Y = (y_1 ,y_2 ,K,y_m )^T$$
(2)
The input of each neuron in the hidden layer is set to Formula 3:
$$b_j = \sum\limits_i = 1^n W_ij x_i – \theta_j $$
(3)
In Formula 3, \(j = 1,2,\Lambda ,k,W_ij\) is the connection weight from the input layer to the hidden layer. \(\theta_j\) is the threshold of the hidden layer neuron y. k is the number of hidden layer units. If the activation function adopts a sigmoid function:
$$f(x) = \frac11 + e^ – x $$
(4)
then the output of the hidden layer unit is as Formula 5:
$$S_j = \frac1{1 + \exp \left( – \sum\limits_i = 1^n W_ij x_i + \theta_j \right)}$$
(5)
The input of each output layer neuron is as Formula 6:
$$C_t = \sum\limits_j = 1^q V_ij S_j – \lambda_t $$
(6)
The output of each output layer neuron is as Formula 7:
$$L_t = \frac1{1 + \exp \left( – \sum\limits_j = 1^q V_jt S_j + \lambda_t \right)}$$
(7)
In Formulas 6 and 7, \(t = 1,2,\Lambda ,q,V_jt\) is the connection weight from the hidden layer to the output layer. t is the output layer unit threshold. In the process of error backpropagation, the single sample error \(E_k\) is as Formula 8:
$$E_k = \frac\sum\limits_t = 1^p (y_t^k – L_t^k )^2 2$$
(8)
The total system error E is as Formula 9:
$$E = \sum\limits_k = 1^m E_k $$
(9)
If both \(E_k\) and E are less than the allowable error, the training process ends; otherwise, the output deviation of each layer of nodes is calculated, and the network connection weights and thresholds are modified. In order to keep decreasing according to the gradient principle, then there is Formula 10:
$$\Delta V_jt = – \alpha \partial E_k /\partial V_jt$$
(10)
From Formula 10, it can be deduced that the weight adjustment of the output layer is as Formula 11:
$$\Delta V_jt = ad_t^k b_j$$
(11)
In Formula 11, \(d_t^k\) is as Formula 12:
$$d_t^k = (y_j^k – L_j^k )t(1 – L_t^k )$$
(12)
\(\alpha\) is the learning rate, and the output layer threshold adjustment amount is as Formula 13:
$$\Delta \lambda = \alpha d_t^k$$
(13)
Similarly, the weight adjustment of the hidden layer is as Formula 14:
$$\Delta W_ij = \beta e_j^k x_i$$
(14)
The threshold adjustment amount of the hidden layer is as Formula 15:
$$\Delta \theta_j = \beta e_j^k$$
(15)
In Formulas 14 and 15, there are \(i = 1,2,\Lambda ,q\), \(j = 1,2,\Lambda ,\textp\) and \(k = 1,2,\Lambda ,m\). Therefore, there is Formula 16:
$$e_j^k = \left( \sum\limits_t = 1^q d_t^k v_jt \right)S_j (1 – S_j )$$
(16)
The weights and thresholds of the output layer and the hidden layer are adjusted according to the derived adjustment amount, so that the entire model completes one training.
The specific implementation process of BP neural network in financial management and risk warning is as follows:
Firstly, collect a large amount of financial management and risk warning related data, and preprocess the data, including data cleaning, standardization, etc. Then, based on the actual problem requirements, determine the structure of the BP neural network, including the number of nodes in the input layer, output layer, and hidden layer. Afterwards, network training is carried out, using sample data to train the network. The weights and thresholds of the network are continuously adjusted through backpropagation algorithms to reduce errors. Finally, predict and evaluate the new data using the trained network, and evaluate the effectiveness of financial management and risk warning based on the prediction results.
-
(2)
Analysis of particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm
Particle swarm optimization is similar to other evolutionary algorithms in which it also uses the concepts of “swarm” and “evolution”. Compared with other evolutionary algorithms, the PSO algorithm adopts evolutionary operation31,32.
If the current position of particle i is \(X_i\), that is, the current flying speed of particle i is \(V_i\), then the best position passed by particle i is \(P_i\), that is, the best fitness value experienced by particle \(i_1\) is called the individual best position. For the convenience of discussion, assuming that \(f(x)\) is the smallest objective function, then the current best position of particle i is determined by Formula 17:
$$P_i (t + 1) = \left\{ \beginarray*20c P_i (t),f(X_i (t + 1)) \ge f(P_i (t)) \\ X_i (t + 1),f(X_i (t + 1)) < f(P_i (t)) \\ \endarray \right.$$
(17)
Assuming that the number of particles in the group is S, and the best position experienced by all particles in the group is \(P_g (t)\), which is called the global best position, then there is Formula 18:
$$P_g (t) \in \left\ P_0 (t),P_1 (t),\Lambda ,P_s (t) \right\\left| f(P_g (t)) \right.$$
(18)
With the above definitions, the evolution formulas of the basic particle swarm algorithm can be described as Formula 19 and Formula 20:
$$vi_j (t + 1) = v_ij (t) + c_1 r_1j (t)[p_ij (t) – x_ij (t)] + c_2 r_2j (t)[p_gj (t) – x_ij (t)]$$
(19)
$$x_ij (t + 1) = x_ij (t) + v_ij (t + 1)$$
(20)
BP neural network has broad application prospects in a wide range of application fields, but its drawbacks are becoming more and more obvious, which seriously restricts the applicability of BP network. Many scholars have made certain improvements to the BP algorithm, but the results obtained are not the same. At present, the most popular method is to combine the BP algorithm with the neural network. It is structurally optimized due to improvements in connection weights, thresholds, etc. Biological intelligence algorithm is one of the most widely used algorithms, such as genetic algorithm, particle swarm algorithm and so on. The local minimization problem of BP network is carried out by genetic algorithm, but it has a large amount of calculation, many network parameters and poor operability, while PSO has better global optimization ability, and on the basis of existing theory, it has better BP network optimization effect.
The specific implementation process of particle swarm optimization algorithm in financial management and risk warning is as follows:
In the implementation process of particle swarm optimization algorithm in financial management and risk warning, firstly, it is necessary to initialize the particle swarm and randomly generate a set of solutions, each corresponding to a parameter or strategy of the financial management and risk warning model. Afterwards, based on the actual needs of the problem, design a fitness function to evaluate the superiority or inferiority of each particle. In financial management and risk warning, fitness functions can be designed based on prediction errors, risk indicators, etc. Next, according to the rules of particle swarm optimization algorithm, update the position and velocity of particles to search for better solutions. In financial management and risk warning, the optimal solution is found by iteratively updating the parameters or strategies of particles. Subsequently, the termination condition is determined to determine whether the algorithm has reached the termination condition, such as reaching the preset maximum number of iterations or finding the optimal solution that meets the requirements. Can we obtain the optimal solution again and apply it to practical financial management and risk warning to improve decision-making effectiveness and risk management level.
Challenges
Because artificial intelligence and big data have inherent biases and limitations, if the data comes from past unfair social structures or decisions, then these data may contain these biases. Machine learning models, especially supervised learning models, inherit biases from their training data. Secondly, due to limitations in data collection, such as web crawlers only being able to crawl information from public web pages, or users being unwilling to share certain sensitive information, the collected data is not comprehensive. In addition, big data also has issues with information accuracy. When the model is too complex or the training data is too sufficient, the model may remember the noise in the training data instead of learning the basic rules of the data. Finally, the interpretability of machine learning models is a challenge. For some complex models, such as deep neural networks, the internal operating mechanisms are difficult to understand intuitively. That is to say, although these models perform well in certain tasks, their decision-making process is “black box”, and it is difficult for people to know why the models make a certain decision.
When dealing with financial datasets, model constraints and potential overfitting issues are particularly important. Financial datasets typically have characteristics such as large data volume, high data dimensionality, non-linear relationships, temporal correlation, high noise, and anomalies. Due to market fluctuations and data collection issues, there may be a large amount of noise and outliers in financial data. These characteristics pose challenges to the constraints and overfitting issues of the model. Due to the high dimensionality and non-linear relationships of financial data, models need to have a certain level of complexity to capture these features. However, excessive complexity may also lead to a decrease in the generalization ability of the model, that is, overfitting the training data and a decrease in the predictive ability of unknown data. Overfitting and underfitting: When training a model, if the model is too complex, it may overfit the training data, resulting in poor performance on new and unseen data. On the contrary, if the model is too simple, it may not be able to capture the complex patterns of the data, resulting in underfitting. In the financial field, overfitting may lead to models fitting past data well, but having poor predictive ability for the future. When dealing with financial datasets, special attention should be paid to the constraints and overfitting issues of the model. By reasonable model selection, preprocessing, feature engineering, and validation, the performance of the model can be maximized and potential risks can be reduced.
Informed consent
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
link

